Overview:
Linear algebra refresher – Part 2/3
This is the second part of the refresher and covers more sophisticated operations and its implementation in Python.
Vector vector multiplication (dot product)
The dot product, also known as the scalar product, is a key operation in linear algebra. It involves multiplying the corresponding components of two vectors and summing up the results.
To calculate the dot product of two vectors u and v, we multiply each component of u with the corresponding component of v and then add up the products. Mathematically, the dot product is denoted as u · v and is calculated as:
u · v = u₁v₁ + u₂v₂ + u₃v₃ + … + uₙvₙ
Here, u₁, u₂, ... uₙ and v₁, v₂, ... vₙ are the individual components of the vectors u and v, respectively.
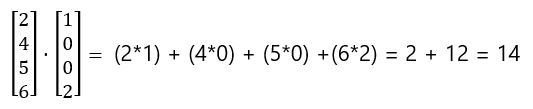
An important use case is the dot product between a transposed vector and a vector, e.g. vTu.

The dot product yields a scalar value, hence the name “scalar product.” It provides information about the similarity or alignment of two vectors. For example, if the dot product of two vectors is zero, it indicates that the vectors are perpendicular or orthogonal to each other. Conversely, a positive dot product suggests that the vectors have a similar direction, while a negative dot product indicates opposite directions.
The dot product has various applications in mathematics and machine learning. It allows us to calculate the angle between vectors, determine vector projections, and perform vector comparisons. In machine learning, the dot product is particularly useful in computing similarity measures, such as cosine similarity, which is commonly used in recommendation systems and natural language processing tasks.
By understanding the dot product, you gain insights into the geometric relationship between vectors and acquire a powerful tool for analyzing and manipulating vector data. This knowledge forms the basis for advanced techniques in linear algebra and machine learning.
Expanding your understanding of vector operations beyond basic scalar vector products, vector vector addition, and vector vector multiplication sets a solid foundation for tackling more complex mathematical concepts and algorithms in the realm of machine learning. These operations serve as essential tools for data transformation, feature engineering, and model optimization.
Remember that while these operations are fundamental to the field, their implementation is often abstracted away by high-level libraries and frameworks. However, having a conceptual grasp of these operations can greatly enhance your ability to optimize and interpret machine learning models, as well as comprehend the underlying mathematical principles.
Implementation in Python
import numpy as np
def vector_vector_multiplication(u, v):
assert u.shape[0] == v.shape[0]
n = u.shape[0]
result = 0.0
for i in range(n):
result = result + u[i] * v[i]
return result
u = np.array([2, 4, 5, 6])
v = np.array([1, 0, 0, 2])
vector_vector_multiplication(u, v)
# Output: 14.0
# dot product is already implemented in numpy
u.dot(v)
# Output: 14.0
Matrix vector multiplication
Matrix vector multiplication is a fundamental operation in linear algebra that involves multiplying a matrix with a vector to produce a new vector.
To perform matrix vector multiplication, we multiply each row of the matrix by the corresponding element of the vector and sum up the results. This process results in a new vector that is a linear combination of the rows of the matrix.
Mathematically, if we have a matrix U and a vector v, the matrix vector multiplication is denoted as Uv and is calculated as:
Uv = (U₁₁v₁ + U₁₂v₂ + ... + U₁ₙvₙ, U₂₁v₁ + U₂₂v₂ + ... + U₂ₙvₙ, ..., Uₘ₁v₁ + Uₘ₂v₂ + ... + Uₘₙvₙ)
Here, U₁₁, U₁₂, ..., Uₘₙ are the individual elements of the matrix U, and v₁, v₂, ..., vₙ are the components of the vector v.

Matrix vector multiplication is a crucial operation in various computational and mathematical applications. It can be used to perform transformations, solve systems of linear equations, and represent linear mappings between vector spaces. In machine learning, matrix vector multiplication is fundamental in performing linear regression, applying weight matrices to input data, and transforming features in neural networks.
Understanding matrix vector multiplication is essential for working with matrices and applying linear transformations in machine learning algorithms. It provides a powerful tool for manipulating and analyzing data in high-dimensional spaces.
Beyond matrix vector multiplication, other important matrix operations in linear algebra include matrix addition, matrix multiplication, and matrix inversion. These operations enable more complex mathematical operations and algorithms, such as solving systems of linear equations, calculating determinants, and finding eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
By expanding your knowledge of matrix operations, you will have a solid foundation for tackling advanced concepts and techniques in machine learning. These operations form the backbone of many algorithms and models used in data analysis and pattern recognition.
Remember that while you may not need to manually perform matrix vector multiplication in your machine learning code, understanding its underlying principles can enable you to optimize your models, troubleshoot potential issues, and make informed decisions about your data and transformations.
Implementation in Python
import numpy as np
def matrix_vector_multiplication(U, v):
assert U.shape[1] == v.shape[0]
num_rows = U.shape[0]
result = np.zeros(num_rows)
for i in range(num_rows):
result[i] = vector_vector_multiplication(U[i], v)
return result
U = np.array([
[2, 4, 5, 6],
[1, 2, 1, 2],
[3, 1, 2, 1]
])
v = np.array([1, 0, 0, 2])
matrix_vector_multiplication(U, v)
# Output: array([14., 5., 5.])
# dot product between vector and matrix is already implemented in numpy
U.dot(v)
# Output: array([14, 5, 5])
Matrix matrix multiplication
Matrix matrix multiplication is a fundamental operation in linear algebra that involves multiplying two matrices to produce a new matrix. This operation enables the transformation and manipulation of data in multidimensional spaces.
To perform matrix matrix multiplication, we multiply each row of the first matrix by each column of the second matrix, and then sum up the results. The resulting matrix has dimensions equal to the number of rows in the first matrix and the number of columns in the second matrix.
Mathematically, if we have two matrices, A and B, the matrix matrix multiplication is denoted as AB and is calculated as:
AB = (A₁₁B₁₁ + A₁₂B₂₁ + … + A₁ₙBₙ₁, A₁₁B₁₂ + A₁₂B₂₂ + … + A₁ₙBₙ₂, …, Aₘ₁B₁₁ + Aₘ₂B₂₁ + … + AₘₙBₙ₁;
A₁₁B₁₂ + A₁₂B₂₂ + … + A₁ₙBₙ₂, A₁₁B₁₂ + A₁₂B₂₂ + … + A₁ₙBₙ₂, …, Aₘ₁B₁ → Aₘ₂B₂₂ + … + AₘₙBₙ₂;
…
A₁₁B₁ₘ + A₁₂B₂ₘ + … + A₁ₙBₙₘ, A₁₁B₁ₘ + A₁₂B₂ₘ + … + A₁ₙBₙₘ, …, Aₘ₁B₁ₘ + Aₘ₂B₂ₘ + … + AₘₙBₙₘ)
Here, A₁₁, A₁₂, ..., Aₘₙ and B₁₁, B₂₁, ..., Bₙₘ are the individual elements of matrices A and B, respectively.
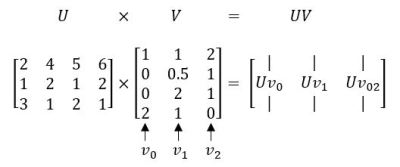
Matrix matrix multiplication is a powerful operation with diverse applications in linear transformations, optimizing systems of equations, and representing complex mathematical operations. In machine learning, matrix matrix multiplication is used in tasks such as matrix factorization, neural network training, and model optimization.
Understanding matrix matrix multiplication is essential for working with large datasets, performing complex transformations, and building advanced machine learning models. It enables you to manipulate, analyze, and process data efficiently in higher-dimensional spaces.
In addition to matrix matrix multiplication, other important matrix operations in linear algebra include matrix addition, scalar matrix multiplication, and matrix transposition. These operations provide the foundation for more complex mathematical techniques, including matrix inversion, eigenvalue decomposition, and singular value decomposition.
By expanding your knowledge of matrix operations, you unlock the ability to tackle advanced concepts and algorithms in machine learning. These operations form the backbone of many modern techniques used in data analysis, pattern recognition, and optimization.
Remember that while you may not need to manually perform matrix matrix multiplication in your machine learning code, understanding its underlying principles is crucial for optimizing and interpreting your models. It empowers you to make informed decisions about data transformations, model architectures, and training strategies.
Implementation in Python
Matrix matrix multiplication is already implemented in libraries such as NumPy. Here is an example of how to perform matrix matrix multiplication using NumPy:
import numpy as np
def matrix_matrix_multiplication(U, V):
assert U.shape[1] == V.shape[0]
num_rows = U.shape[0]
num_columns = V.shape[1]
result = np.zeros((num_rows, num_columns))
for i in range(num_columns):
vi = V[:, i]
Uvi = matrix_vector_multiplication(U, vi)
result[:, i] = Uvi
return result
U = np.array([
[2, 4, 5, 6],
[1, 2, 1, 2],
[3, 1, 2, 1]
])
V = np.array([
[1, 1, 2],
[0, 0.5, 1],
[0, 3, 1],
[2, 1, 0]
])
matrix_matrix_multiplication(U, V)
# Output:
#array([[14. , 25. , 13. ],
# [ 5. , 7. , 5. ],
# [ 5. , 10.5, 9. ]])
# dot product between matrix and matrix is already implemented in numpy
U.dot(V)
# Output:
#array([[14. , 25. , 13. ],
# [ 5. , 7. , 5. ],
# [ 5. , 10.5, 9. ]])
In this example, U and V are two matrices that we want to multiply. The np.dot() function performs the matrix matrix multiplication, and the result is a new matrix.
Matrix matrix multiplication is a fundamental operation that opens the door to a wide range of mathematical techniques and algorithms. By grasping its principles and implementing it in your code, you can harness the power of linear algebra in your machine learning projects.
